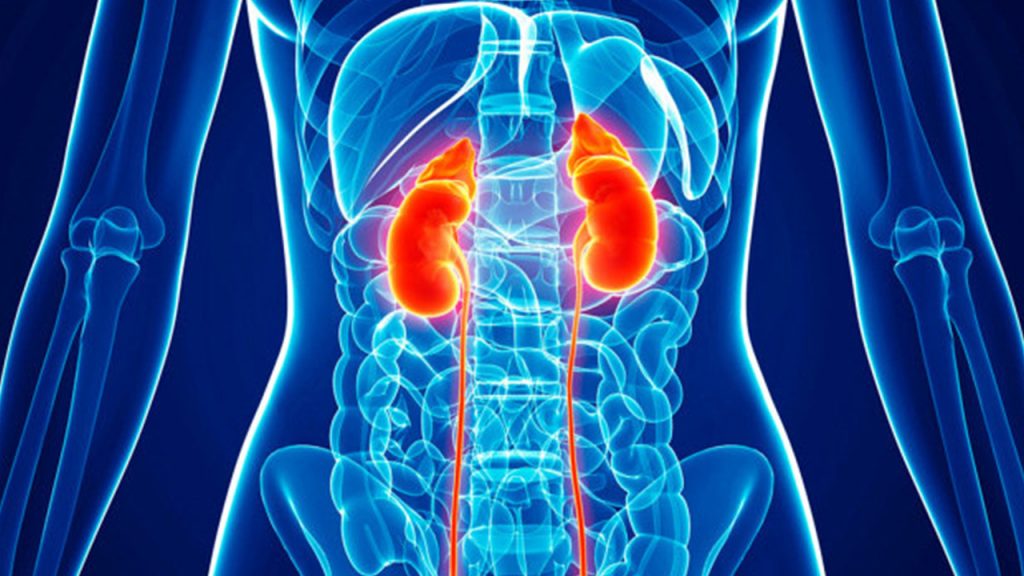
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) or chronic renal disease, is a condition that occurs when your kidneys don’t work as well as they should to filter waste, toxins and excess fluid from your body. Kidney disease progresses in stages—defined by a blood test (eGFR) to determine how well your kidneys are working to clean your blood—and may eventually lead to kidney failure. The goal of treating CKD is to manage your health at every stage, which can help slow progression and keep your kidneys functioning as long as possible. Treatment options for kidney failure include dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Kidney disease is hard to detect early because most symptoms of kidney disease don’t show up until later stages. CKD symptoms may include fatigue, changes in urination, itching or swelling of the hands or feet.
There are some factors that put you at a higher risk for CKD, including family history, health conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure, ethnicity or overuse of medications.
